JDBC Basic
➤ Intro to JDBC
➤ JDBC vs ODBC
➤ JDBC API
➤ JDBC Driver
Connect to Database
➤ Oracle Connection
➤ MySQL Connection
➤ Using Eclipse IDE
➤ Coding Standards
➤ Close JDBC Object
➤ Java.sql Package
➤ DriverManager Class
➤ Get Connection
JDBC Statement
➤ Statement Interface
➤ Statement Example
➤ Create a database
PreparedStatement
➤ Types of statements
➤ PreparedStatement
➤ Statement vs PreParedStatement
PreparedStatement Example
➤ Insert record
➤ Update record
➤ Select record
➤ Create a table
➤ More Examples
➤ Surrogate Key
Others
➤ DatabaseMetaData
➤ ResultSetMetaData & ParameterMetaData
In this post, we will discuss how to establish the JDBC connection in Java with MySQL database. After establishing the connection we will develop a sample JDBC application to check whether the connection is done properly or not with the MySQL database. We will develop a simple JDBC program to fetch the record from one table of the MySQL database and display it on the console.
Before establishing a MySQL database connection in Java, make sure you have the following software setup ready on your computer system,
1) MySQL Database
2) JDK1.8 or later version
3) Any text editor to write the code or IDE
The MySQL server version, connector version, JDBC version and required JDK
| Connector/J Version | JDBC Version | MySQL Server Version | Required JDK |
| 5.1 | 3.0, 4.0, 4.1, 4.2 | 5.6, 5.7, 8.0 | JDK 5, JDK 8 or higher |
| 8.0 | 4.2 | 5.6, 5.7, 8.0 | JDK 8 or higher |
Establish MySQL Database Connection
Now let us begin the establishing MySQL JDBC connection.
Step1) Collect JDBC driver of MySQL database.
The JDBC driver of MySQL database doesn’t come along with MySQL database installation, We need to collect it separately. Download the JDBC driver/connector of the MySQL database.
Open the zip file, and extract it. The mysql-connector-java-<version>.jar is the main jar file that will be used to develop the JDBC applications through the MySQL database.
Step2) Add jar file to the CLASSPATH.
Note:- In the CLASSPATH don’t add the location/folder where the jar file is available. We have to add the location of the jar file, not the folder where the jar file is available.
Don’t try to write the location name manually because we can do a spelling mistake, so it is recommended to copy the jar file location. In order to copy the jar files correctly in the Windows operating system, Go to the folder where the jar file is locating, now select jar file, right-click and select properties, in the security section you will find “Object name”. We can copy the actual path of the jar file from here.
For example:- In my case,
The folder where the Jar file is located:- C:\Users\user\Downloads\
The location which will be added to Classpath:- C:\Users\user\Downloads\mysql-connector-java-8.0.21.jar
How to add the jar file to the classpath?
For this, we have to go to “Advance System Settings”. There are many ways to go to “Advance System Settings”,
1) This PC -> Properties -> Advance System Settings
2) Control panel -> System and Security -> System -> Advance system settings
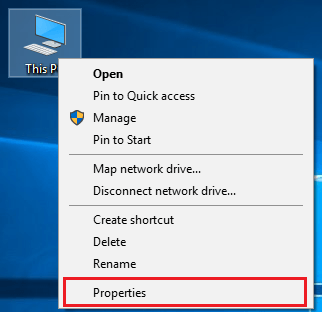
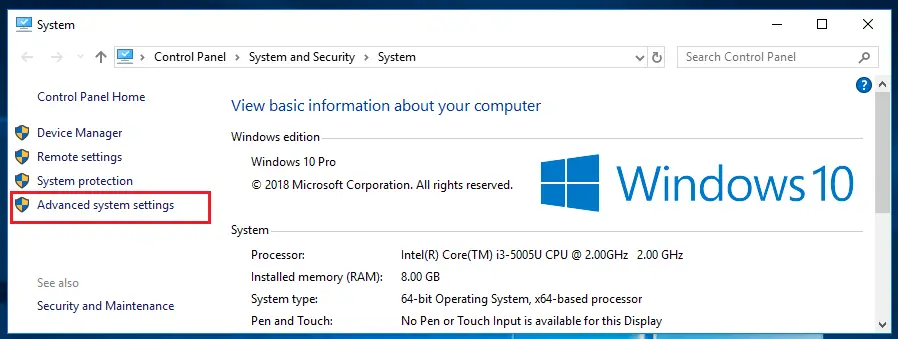
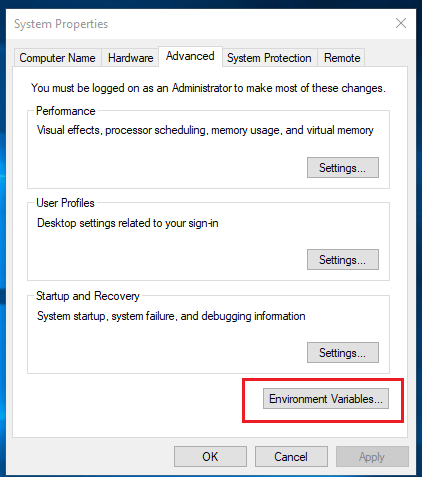
Now go to Advance system settings -> Environment Variables -> System Variables.
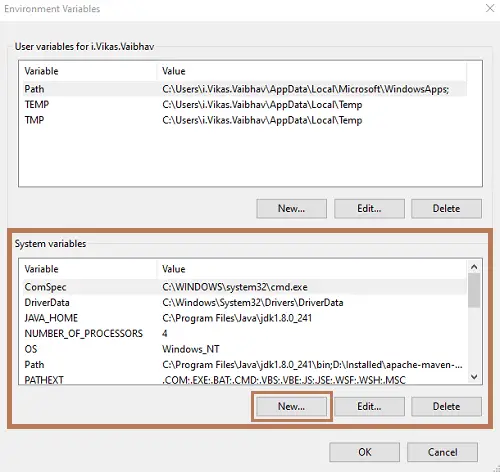
If the CLASSPATH variable already exists then “Edit it”, otherwise create “New”.
In case of “New”
Variable Name: CLASSPATH
Value: <location-of-oracle-jdbc-jar-file>;.In case of “Edit”
Variable Name: CLASSPATH
Value: <location-of-oracle-jdbc-jar-file>;<existing-values>;.It is recommended to place dot (.) after the variable values, and ; is a separator that separates two variable values. Learn more:- Different Ways to Set Java Classpath Environment Variables in Windows
In case of “Edit”, if new window came then each line must have separate variable value, and using “Move UP” button place it on the first position.
Step3) Develop the application.
We have established the connection successfully. Now, we have to develop a sample JDBC application to check the establishing the connection is done properly or not.
Also See:-
MySQL JDBC Driver Details
We need some basic details of MySQL JDBC driver to develop the JDBC program.
JDBC Driver Class Name:: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
URL::
- For local MySQL::
jdbc:mysql:///<logical-database-name> - For remote MySQL::
jdbc:mysql://<host>:<port-no>/<logical-database-name>
Username: <username-of-the-MySQL-database>
Password: <password-of-the-MySQL-database>
Note:- If you developing JDBC application for first time in local computer/laptop then use URL for local MySQL.
How to find the database name in MySQL?
Type below query to get all databases available in the MySQL server.
show databases;If you are new to MySQL then create a new database,
CREATE SCHEMA `knowprogram` ;Here “knowprogram” will be the name of the database. Hence the URL for local MySQL will be => jdbc:mysql:///knowprogram
MySQL Database JDBC Connection Code in Java Example
Now, let us develop a small Java program to check JDBC connection with MySQL Database is established properly or not?
import java.sql.*;
public class ConnectionTest {
public static void main(String[] args ) throws Exception {
// register Oracle thin driver with DriverManager service
// it is optional for JDBC4.x version
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// declare variables
// place your own values
final String url = "jdbc:mysql:///knowprogram";
final String user = "root";
final String password = "Password@0";
// establish the connection
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// display status message
if(con == null) {
System.out.println("JDBC connection is not established");
return;
}
else
System.out.println("Congratulations,"+
" JDBC connection is established successfully.\n");
// close JDBC connection
con.close();
} //main
} //classCompile the Java Program,> javac ConnectionTest.java
Execute the program,> java ConnectionTest
Congratulations, JDBC connection is established successfully.
Standard Steps to Develop JDBC Application
There are some standard steps to develop JDBC program. Every JDBC program will have these common points.
1. Register JDBC driver with DriverManager service
This step is only required for the JDBC3.0 The JDBC4.x version supports the auto-loading of the driver class, so registering JDBC driver with DriverManager is optional. Here auto-loading means when we call the method of the class then due to logic of its static block it loads the driver class.
// register MySQL connector with
// DriverManager service
// optional for JDBC4.x version drivers
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");2. Establish the connection with database software
// establishing the connection with database software
Connection con =
DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);Here place your own URL, username, and password which are assigned to the MySQL database.
3. Create JDBC Statement object
// create JDBC Statement object
Statement st = con.createStatement();4. Gather SQL query result back to Java application from database software.
5. Close JDBC objects.
// close JDBC objects
rs.close();
st.close();
con.close();JDBC Program Example
Previously, we have developed a simple Java program to check that the JDBC connection is established properly with the MySQL database or not. Now, let us develop a simple Java to fetch records from a table and display it on the console.
But for this, we need a table. You can use an existing table. But here we are developing for the first time so we will create a new table in the MySQL database.
Create table,
CREATE TABLE `knowprogram`.`student`(
`sno` INT NOT NULL,
`sname` VARCHAR(45) NULL,
`sadd` VARCHAR(45) NULL,
`avg` FLOAT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`sno`)
);Table created. Now, insert some record into the table,
INSERT INTO `knowprogram`.`student` (`sno`, `sname`, `sadd`, `avg`) VALUES ('10', Sophia', 'Manchester', '70');
INSERT INTO `knowprogram`.`student` (`sno`, `sname`, `sadd`, `avg`) VALUES ('11', 'William', 'Washington', '80');
INSERT INTO `knowprogram`.`student` (`sno`, `sname`, `sadd`, `avg`) VALUES ('12', 'Alex', 'Boise', '85');
INSERT INTO `knowprogram`.`student` (`sno`, `sname`, `sadd`, `avg`) VALUES ('13', 'Amelia', 'London', '90');Now, the table is ready,
| sno | sname | sadd | avg |
| 10 | Sophia | Manchester | 70 |
| 11 | William | Washington | 80 |
| 12 | Alex | Boise | 85 |
| 13 | Amelia | London | 90 |
Java Program
We will develop a simple JDBC program which will fetch the record of “student” table and display it to the console.
import java.sql.*;
public class SelectTest {
public static void main(String[] args ) throws Exception {
// variables
final String url = "jdbc:mysql:///knowprogram";
final String user = "root";
final String password = "Password@0";
// establish the connection
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
// create JDBC statement object
Statement st = con.createStatement();
// prepare SQL query
String query = "SELECT SNO, SNAME, SADD, AVG FROM STUDENT";
// send and execute SQL query in Database software
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(query);
// process the ResultSet object
boolean flag = false;
while(rs.next()) {
flag = true;
System.out.println( rs.getInt(1) + " " + rs.getString(2) +
" " + rs.getString(3) + " " + rs.getFloat(4) );
}
if(flag == true) {
System.out.println("\nRecords retrieved and displayed");
} else {
System.out.println("Record not found");
}
// close JDBC objects
rs.close();
st.close();
con.close();
} //main
} //classCompile and Execute the JDBC program,
> javac SelectTest.java
> java SelectTest
Output:-
10 Sophia Manchester 72.0Records retrieved and displayed
11 William Washington 80.0
12 Alex boise 95.0
13 Amelia London 85.0
Note:- While developing this application we didn’t follow any coding standards. We should follow some coding standards while developing JDBC applications. Learn more:- Coding Standards and Guidelines for JDBC Application, Best Way to Close JDBC Connection Object
If you enjoyed this post, share it with your friends. Do you want to share more information about the topic discussed above or do you find anything incorrect? Let us know in the comments. Thank you!
Also Learn,